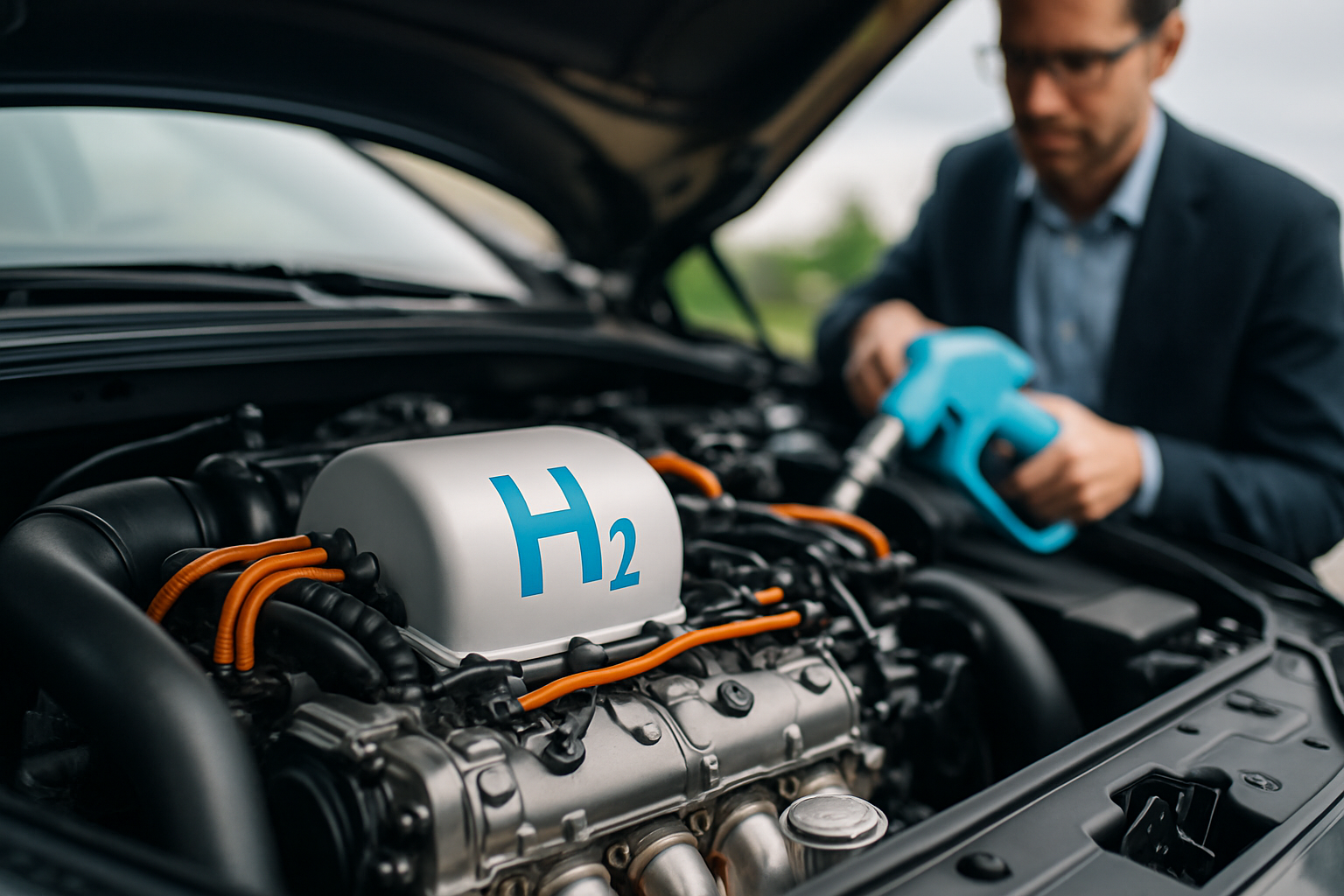
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Vehicles: The Next Frontier in Clean Mobility
In the ever-evolving landscape of automotive technology, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) are emerging as a promising solution for sustainable transportation. This cutting-edge technology harnesses the power of hydrogen to produce electricity, offering zero-emission driving with the convenience of quick refueling. As the world grapples with climate change and seeks alternatives to fossil fuels, FCVs present an intriguing option that combines environmental benefits with practical usability.

Infrastructure Challenges and Solutions
One of the primary hurdles facing widespread FCV adoption is the lack of hydrogen refueling infrastructure. Unlike the ubiquitous network of gas stations, hydrogen filling stations are still relatively scarce. However, several countries and private companies are investing heavily in expanding this infrastructure. Japan, for instance, has committed to building a hydrogen society, with plans for hundreds of refueling stations across the country by 2025.
Performance and Range Advantages
FCVs offer several advantages over traditional electric vehicles (EVs). Refueling a hydrogen tank takes just a few minutes, comparable to filling up a gas tank, addressing the long charging times associated with EVs. Additionally, FCVs typically offer greater range than most current EVs, with some models capable of traveling over 400 miles on a single tank of hydrogen.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
While FCVs produce zero emissions at the tailpipe, the environmental impact of hydrogen production is a crucial consideration. Currently, most hydrogen is produced from natural gas through a process called steam methane reforming, which does generate carbon emissions. However, there’s growing interest in green hydrogen production methods, such as electrolysis powered by renewable energy sources like wind or solar. As these cleaner production methods scale up, the overall environmental footprint of FCVs will continue to improve.
Automotive Industry Investment and Future Prospects
Major automakers are increasingly investing in hydrogen fuel cell technology. Toyota, Hyundai, and Honda have already released commercial FCV models, with others in development. These manufacturers see FCVs as a complementary technology to battery electric vehicles, particularly suitable for larger vehicles like trucks and buses where battery weight becomes a significant factor.
Challenges in Cost and Efficiency
Despite their potential, FCVs face challenges in terms of cost and efficiency. The complex technology and use of precious metals in fuel cells make FCVs more expensive to produce than conventional vehicles or EVs. Additionally, the overall energy efficiency of FCVs is currently lower than that of battery electric vehicles, primarily due to losses in hydrogen production and compression.
Fuel Cell Technology Beyond Passenger Vehicles
The applications of hydrogen fuel cell technology extend beyond personal transportation. In the heavy-duty sector, fuel cells are being explored for long-haul trucks, trains, and even maritime vessels. These applications leverage the quick refueling and long-range capabilities of hydrogen, addressing some of the limitations of battery electric powertrains in these demanding use cases.
Policy Support and Government Initiatives
Government support plays a crucial role in the development and adoption of FCVs. Countries like Japan, South Korea, and Germany have implemented policies to promote hydrogen technology, including subsidies for FCV purchases and investment in refueling infrastructure. In the United States, California has been at the forefront of supporting FCVs, offering incentives and working to expand the hydrogen station network.
The Role of FCVs in a Multi-Technology Future
As the automotive industry transitions towards cleaner technologies, it’s becoming clear that no single solution will dominate. FCVs are likely to play a significant role alongside battery electric vehicles and other alternative powertrains. This diversity in clean mobility options will allow for a more flexible and resilient transportation ecosystem, capable of meeting varied needs and preferences.
Overcoming Public Perception and Safety Concerns
One of the challenges facing FCV adoption is public perception, particularly regarding the safety of hydrogen as a fuel. While hydrogen is highly flammable, extensive safety measures are incorporated into FCV design and hydrogen handling systems. Educating the public about these safety features and the overall benefits of FCVs will be crucial for wider acceptance.
In conclusion, hydrogen fuel cell vehicles represent an exciting frontier in automotive technology. While challenges remain in infrastructure development, cost reduction, and efficiency improvements, the potential benefits of FCVs in terms of quick refueling, long range, and zero emissions make them a compelling option for the future of clean mobility. As technology advances and support grows, FCVs may well become a common sight on our roads, contributing to a more sustainable transportation landscape.